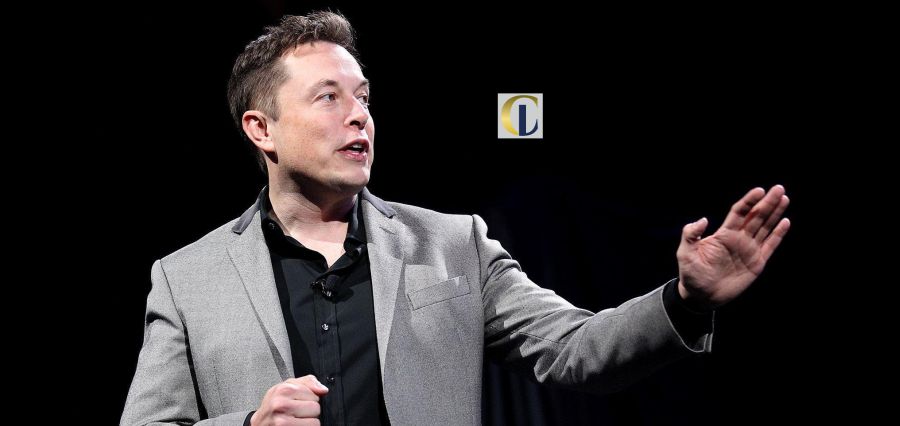
Amidst challenges in China where local competitors have gained an edge, grappling with technological disruptions in the industry, and experiencing a general downturn in demand, Elon Musk views the Indian market as crucial as India views the electric vehicle (EV) narrative. As Musk prepares to touch down in India this month to unveil his EV investment plans, he anticipates a warm welcome but also acknowledges potential hurdles.
India anticipates Tesla’s arrival, akin to its impact in China, to catalyse the domestic electric vehicle market. Despite rejecting Tesla’s request for upfront import duty reductions two years ago, India now sees value in recent concessions, coupled with commitments for future investment and local production targets.
Key issues shaping discussions with Tesla include:
Policy Adjustment: India’s revised EV policy lowers import duties to 15% for car models priced over $35,000, contingent on a $500 million local factory investment commitment. This shift represents a partial reversal of previous manufacturing incentives, allowing carmakers to import fully built vehicles with a pledge to establish local production facilities later. While Tesla initially sought imports from its Shanghai factory, India’s preference is reportedly for deliveries from its Berlin-Brandenburg facility.
Subsidy Structure: Duty waivers apply to electric cars priced at $35,000 or higher, a segment typically ineligible for tax exemptions. While import volumes may be capped annually, Tesla desires to gauge market interest through car sampling before committing to large-scale manufacturing.
The Ministry of Commerce views the policy as an effort to attract global EV investments, enhance technology access for Indian consumers, bolster the Make in India initiative, foster healthy competition, reduce oil imports, and combat air pollution.
Last year, the Indian government reportedly rejected a $1 billion EV plant proposal by China’s BYD, potentially due to security concerns.
Industry Dynamics: The EV sector faces significant challenges, with Tesla particularly affected by global demand slowdowns. Lower production and delivery rates have led to stock declines, reflecting broader market trends impacting other manufacturers like GM and Ford.
As Tesla prepares to enter the Indian market, both parties navigate a landscape marked by policy adjustments, subsidy structures, and broader industry shifts, underscoring the significance of this pivotal moment in the EV sector’s evolution.
Tesla faces three primary challenges:
Affordable Entry-Level Car: Elon Musk initially envisioned Tesla’s mission to include the creation of a mass-market, entry-level “low-cost family” car, but this remains unfulfilled. While the Model 3 sedan serves as the company’s cheapest option, priced at nearly $40,000 in the US, the planned low-cost Model 2 has yet to materialize.
Competition from Chinese EV Makers: Less prominent Chinese electric vehicle manufacturers are rapidly narrowing the gap with Tesla. Shenzhen-based BYD surpassed Tesla as the leading seller of electric cars in the final three months of 2023. This surge was fueled by strong sales of BYD’s smaller, more affordable EV models like the Seagull and Dolphin.
Charging Network Accessibility: Tesla’s extensive and reliable charging network in the US, parts of Europe, and China has historically been exclusive to Tesla owners. However, the company is now obligated to partially open its 45,000-charger network in the US to all electric car models by the end of 2024 to access $7.5 billion in subsidies. This move erodes Tesla’s advantage in offering a proprietary and efficient fast charging network.